Overview
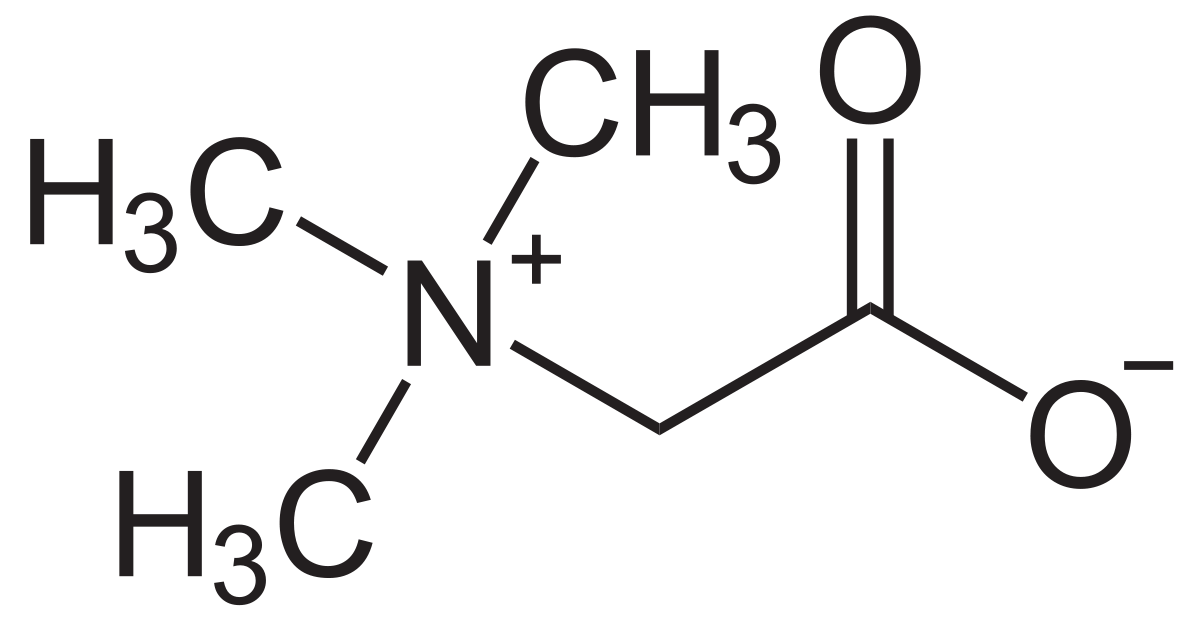
Betaine, also called betaine anhydrous, or trimethylglycine (TMG), is a substance that’s made in the body. It’s involved in liver function, cellular reproduction, and helps to make carnitine. It also helps the body metabolize an amino acid called homocysteine.
Betaine anhydrous can also be found in foods such as beets, spinach, cereals, seafood, and wine.
Betaine anhydrous helps the body to process a chemical called homocysteine. Homocysteine is involved in the normal function of many different parts of the body, including blood, bones, eyes, heart, muscles, nerves, and the brain. Betaine anhydrous prevents the buildup of homocysteine in the blood.
A specific betaine anhydrous prescription product (Cystadane) is FDA-approved for the treatment of high urine levels of homocysteine (homocystinuria). People also use non-prescription betaine anhydrous supplements for reducing blood and urine homocysteine levels, athletic performance, depression, dry mouth, and many other purposes, but there is no good scientific evidence to support most of these uses.
Get further information on Nicotinamide Mononucleotide and Resveratrol.